Join Our Social Media
For Even More Exclusive Content!
TV & Film
View more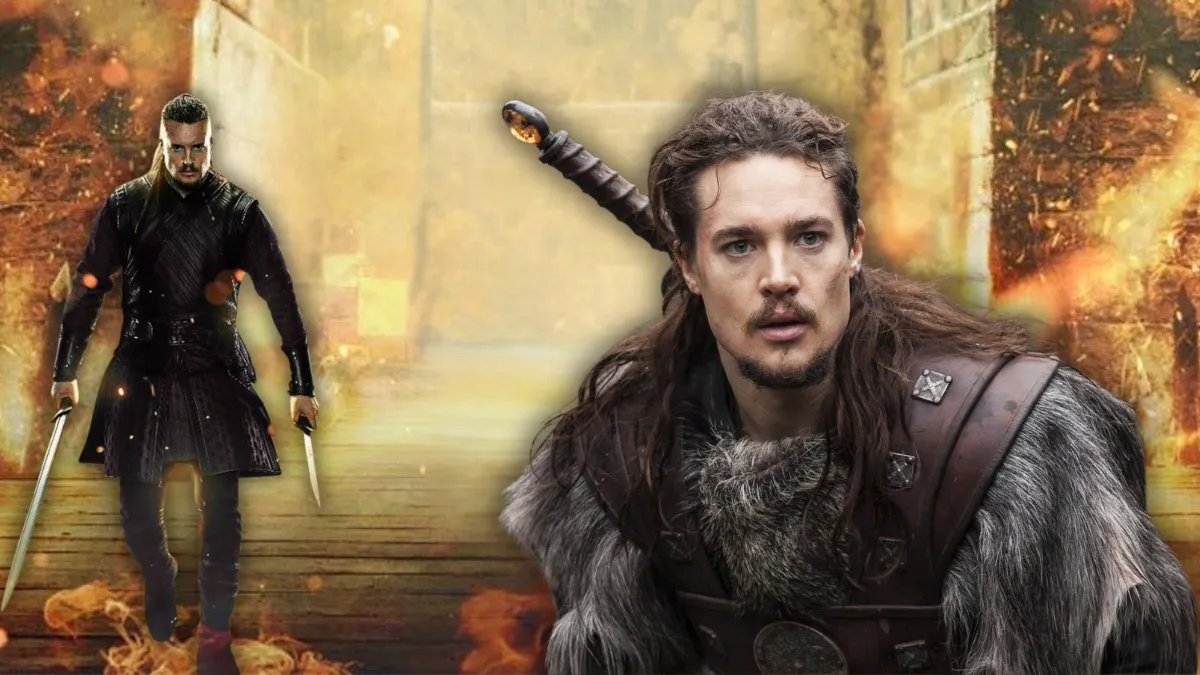
Viewers Declare This Netflix Show ‘Better Than Game of Thrones’ After Epic Finale
Viewers tuning into Netflix in recent months have felt something different. Some say it’s not just another medieval drama. Whispers …
Celebrity
View moreEntertainment
View more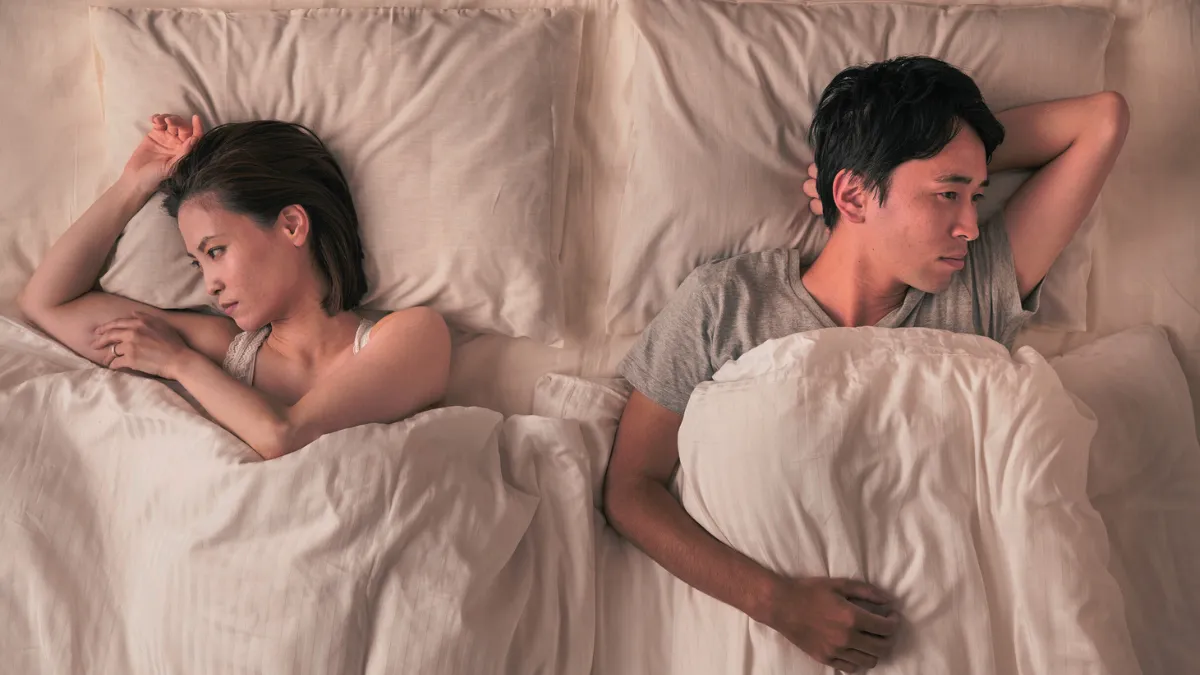
A Surprisingly Common Bedroom Kink That Millions Of Women Want But Men Overlook
For many couples, bedroom conversations tend to focus on variety, technique, or trying something new. Yet growing evidence suggests that …