NASA has issued a critical warning about a massive asteroid that could pose a catastrophic threat to millions of people worldwide.
The asteroid, named 2024 YR4, was discovered in December 2024 by Chile’s Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System. Since then, it has been under close observation due to its potential impact risk.
Measuring between 40 to 90 meters in diameter, 2024 YR4 has captured the attention of astronomers and space agencies worldwide. Scientists have been carefully monitoring its trajectory to determine the likelihood of an impact with Earth.

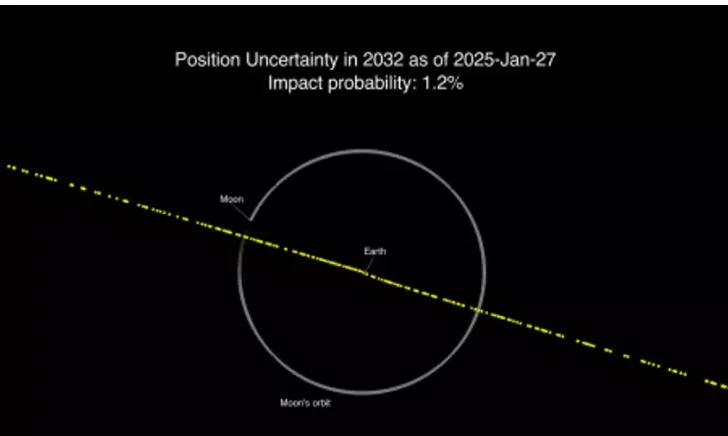
Early estimates placed the probability of collision at just 1%, but recent calculations have shown an alarming increase. NASA reported that the chance of impact had risen to 3.1%—the highest recorded risk for an asteroid in modern tracking history.
This significant development has intensified discussions on planetary defense strategies and the potential measures that could be taken to prevent a disaster. Experts have drawn comparisons to the Tunguska event of 1908, when an asteroid of similar size flattened over 830 square miles of Siberian forest.
The energy released by 2024 YR4, if it were to collide with Earth, is estimated to be 500 times more powerful than the atomic bomb dropped on Hiroshima. Such an event could cause devastating destruction, particularly if it were to strike a densely populated area.

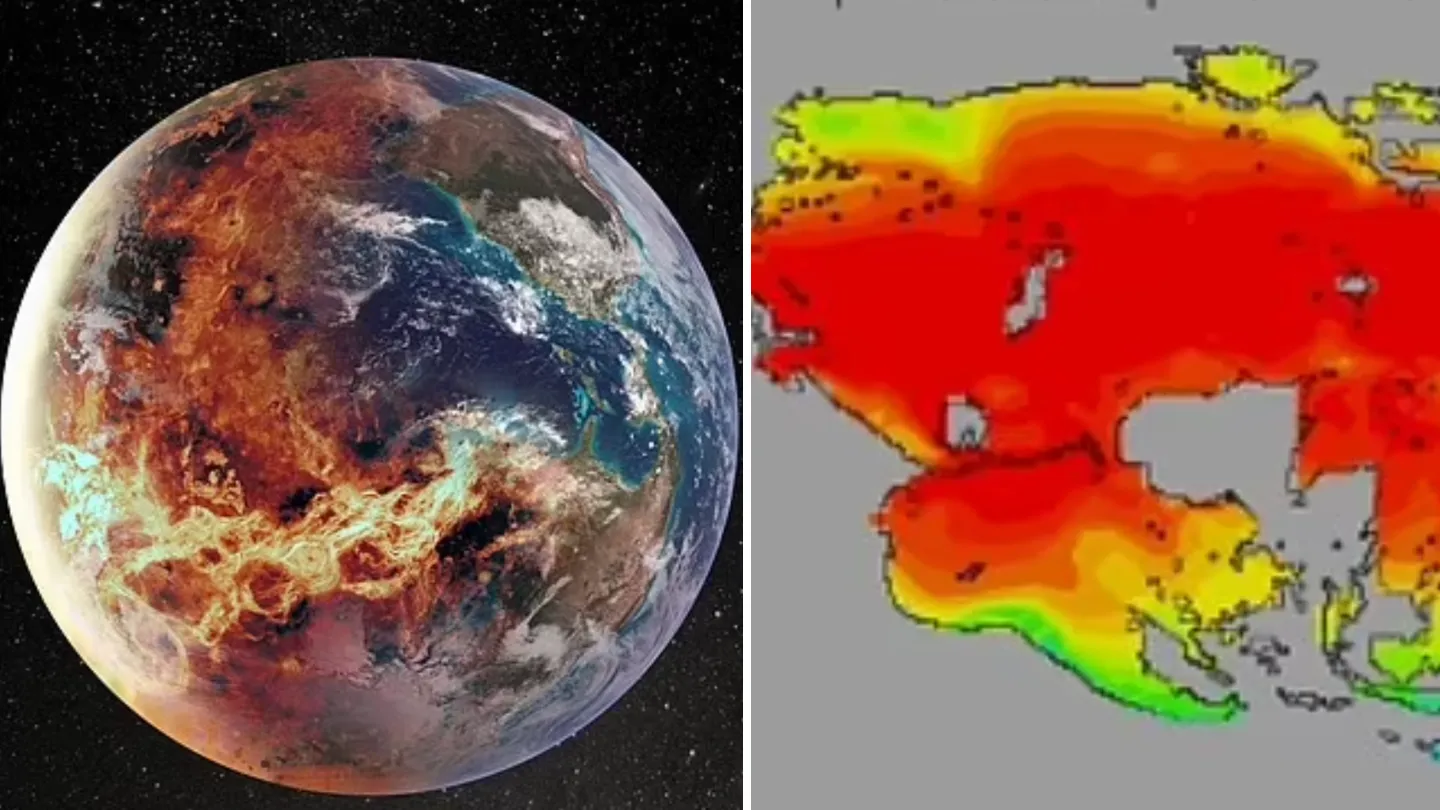
Scientists have mapped a risk corridor for the asteroid, which spans multiple continents. This impact zone includes some of the world’s most populated cities, putting over 100 million people at risk.
The projected trajectory of 2024 YR4 starts over the Pacific Ocean and moves across South America, the Atlantic Ocean, Africa, and parts of South Asia. Major urban centers like Bogotá, Lagos, Mumbai, and Dhaka fall within this impact path, raising concerns about potential casualties and infrastructure damage.
The asteroid’s approach has sparked urgent discussions among space agencies about possible defense mechanisms. One promising solution is the kinetic impactor technique, which was successfully demonstrated in 2022 during NASA’s DART mission.

The DART mission involved crashing a spacecraft into an asteroid to alter its course, proving that deflection is a viable method for planetary defense. Experts believe a similar approach could be considered for 2024 YR4 if its impact risk continues to increase.
Meanwhile, NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA) have ramped up efforts to refine their calculations and monitor the asteroid’s behavior. Scientists stress that improving estimates of the asteroid’s exact size and composition is critical to assessing the real threat it poses.
Astronomers have been using powerful telescopes, including the James Webb Space Telescope, to study 2024 YR4 with greater accuracy. More precise measurements will determine whether intervention is necessary and how best to handle the situation.

Now, after months of intense monitoring, new calculations have dramatically changed the outlook. NASA has significantly downgraded the asteroid’s impact probability to just 0.004%, effectively eliminating immediate concerns of a collision in 2032.
While the threat level has decreased, experts caution that constant vigilance is necessary. The unpredictable nature of space objects means that continued observation and preparedness are essential.
The case of 2024 YR4 has reinforced the importance of global cooperation in planetary defense. Space agencies worldwide must remain proactive in tracking and mitigating asteroid threats before they become imminent dangers.
Though Earth has been spared this time, scientists warn that future asteroids could pose even greater risks. The lessons learned from 2024 YR4 will shape the strategies needed to protect our planet from cosmic threats.
NASA reassures the public that while no immediate danger exists, efforts to enhance planetary defense capabilities will continue. As space agencies refine their techniques, humanity is gradually gaining the ability to prevent an asteroid catastrophe.

The world may have avoided a disaster, but this close call serves as a reminder that the threat from space is always real and that preparation is the key to survival.
Feature Image Credit: (NASA)